Introduction
The Taj Mahal, nestled alongside the banks of the Yamuna River in Agra, India, stands as an everlasting testimony to like and architectural brilliance. Often known as the “Jewel of Muslim Art in India,” this ivory-white mausoleum isn’t always remarkable a surprise of Mughal form but a profound brand of romance, information, and way of lifestyle. Every three hundred and sixty-five days, hundreds of masses of internet net site online net page net site traffic from in some unspecified time inside the future of the globe are interested in its ethereal beauty, making it one of the most visited landmarks within the globe. Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983, the Taj Mahal keeps captivating hearts and encourages awe, maintaining its recognition as one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
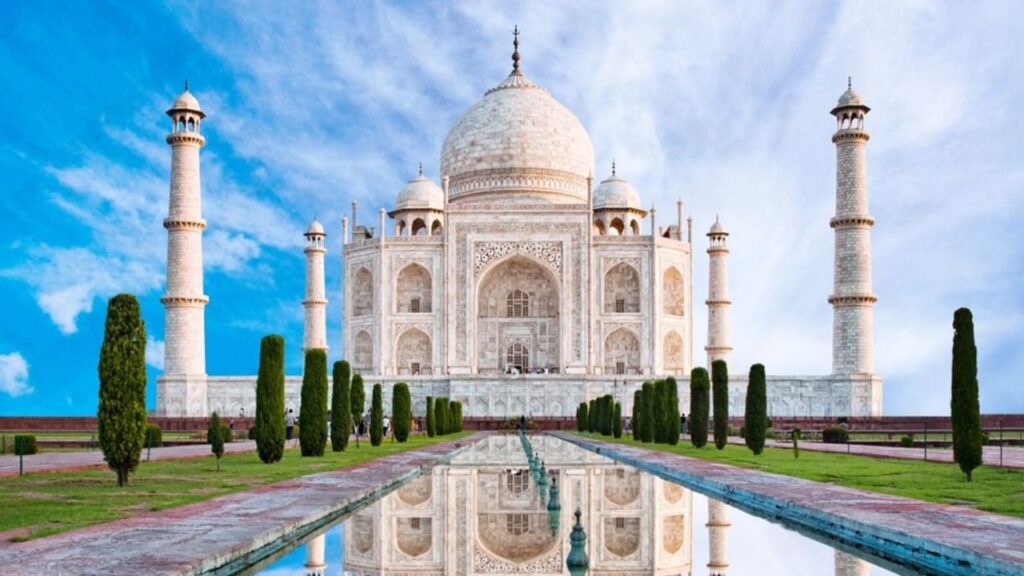

The History of the Taj Mahal
Who Built the Taj Mahal and Why?
Commissioned using Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in 1632, the Taj Mahal ended up conceived as a mausoleum to honor his beloved accomplice, Mumtaz Mahal. She tragically passed away sooner or later from childbirth, leaving the emperor devastated. In her reminiscence, Shah Jahan predicted a shape that could constitute their eternal love, and the Taj Mahal ended up that immortal monument.
Historical Context During Mughal Rule
The 17th century marked the zenith of the Mughal form, characterized by grandeur, symmetry, and present-day innovation. Under Shah Jahan’s reign, the empire saw a surge in cultural and architectural accomplishments, with the Taj Mahal becoming the crowning jewel of this period. Its production spanned over a few years, with hundreds of artisans, architects, and people contributing to its introduction.
Key Figures in Its Construction
The introduction of the Taj Mahal introduced collectively some of the brilliant minds of the time. Ustad Ahmad Lahori, a famous architect, is often credited due to the reality the chief fashion style fashion designer. Persian, Indian, and Islamic architectural effects seamlessly merged to create this masterpiece, reflecting the collaborative genius of the generation.
Architectural Splendor
Design and Layout
The Taj Mahal is an epitome of symmetry and precision. The complex includes a lovable applicable dome flanked with the beneficial resource of 4 minarets, a mosque, a guesthouse, and luxurious gardens divided with the beneficial aid of water channels. Its layout follows the Persian concept of a “paradise lawn,” representing an idealized imaginative and prescient of heaven.
Materials Used
Constructed generally of white Makrana marble, the Taj Mahal furthermore consists of semi-valuable stones like jade, turquoise, and lapis lazuli, sourced from unique factors of the region. These substances lend the form of a shimmering super, which adjusts sun solar sunglasses based totally in reality surely on the time of day and moonlight.
Intricate Craftsmanship
The complicated carvings, floral motifs, and calligraphy decorating the partitions are a testament to the artisans’ competencies. Verses from the Quran are inscribed with incredible precision, and black marble inlay is used on the white marble floor. The combination of geometric and floral designs highlights the Mughal penchant for perfection.
Symbolism and Cultural Significance
A Symbol of Eternal Love
The Taj Mahal is notably seen as a photo of undying love. Its advent came to be pushed with the beneficial beneficial beneficial aid of Shah Jahan’s devotion to Mumtaz Mahal, encapsulating a tale that transcends time and cultures.
Religious and Artistic Significance
Beyond its romantic connotations, the Taj Mahal holds nonsecular significance. The complex Quranic inscriptions and the use of Islamic architectural requirements mirror its spiritual essence. It is also celebrated as a pinnacle of Mughal paintings, combining Persian, Indian, and Central Asian effects.
Depictions in Literature, Art, and Cinema
From poetry and novels to Bollywood and Hollywood films, the Taj Mahal has inspired endless modern works. Its airy beauty regularly serves as a metaphor for perfection, purity, and passion.
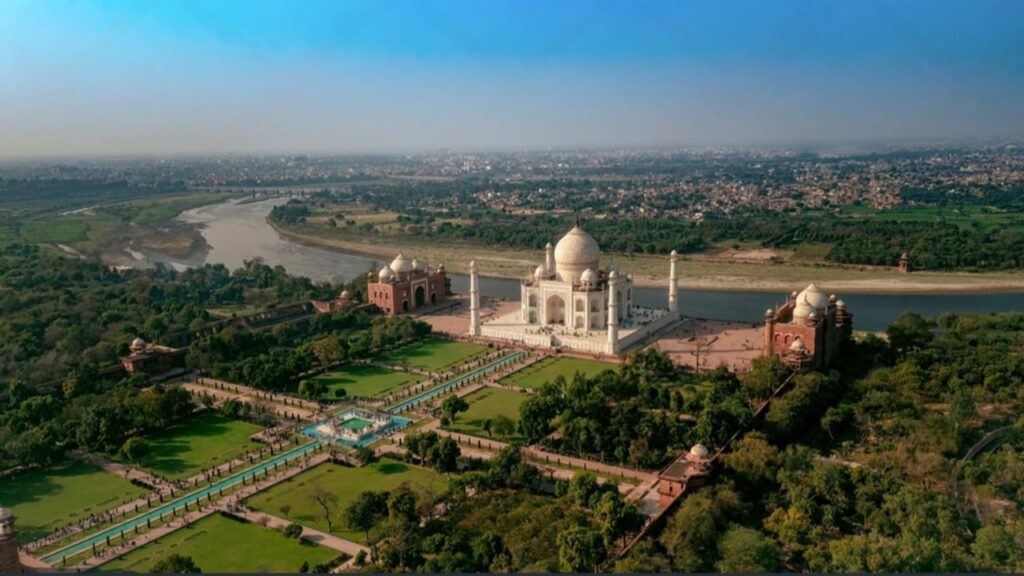

Conclusion
The Taj Mahal is a prolonged manner more than first-rate a superb shape; it’s far a timeless ode to love, artwork, and human ingenuity. Its top-notch splendor, ancient significance, and cultural symbolism have solidified its vicinity as a modern-day icon. Visitors from around the vicinity wonder at its tough layout and are touched by the transferring tale inside the back of its introduction. However, with its reputation comes the responsibility to keep this treasure for future generations. Sustainable tourism, combined with ongoing protection efforts, is important to safeguard its legacy.
FAQs
2. What is the best time to visit the Taj Mahal?
The best time to visit is during sunrise or sunset, between October and March, when the weather is pleasant.
3. Are there any restrictions for visitors?
Yes, items like food, large bags, and drones are prohibited. Visitors must also follow designated paths to protect the monument.
4. How is the Taj Mahal being preserved?
Efforts include regular cleaning, restricted pollution in the area, and government measures to control visitor numbers and protect its surroundings.
5. What makes the Taj Mahal unique?
Its exquisite symmetry, white marble construction, intricate inlay work, and the romantic story behind its creation make it truly one of a kind.



Leave a Reply